Flux GitOps Cheatsheet with Real-World Example
Understanding GitOps
GitOps is an operational framework that uses Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application deployments. Both Flux CD and Argo CD are popular GitOps tools that help automate Kubernetes deployments.

Flux is a GitOps operator that keeps your Kubernetes cluster in sync with configuration in git. It automates deployments by monitoring your repository and applying changes when detected
Prerequisites
- A Kubernetes cluster
fluxCLI installed- GitHub personal access token (for repository access)
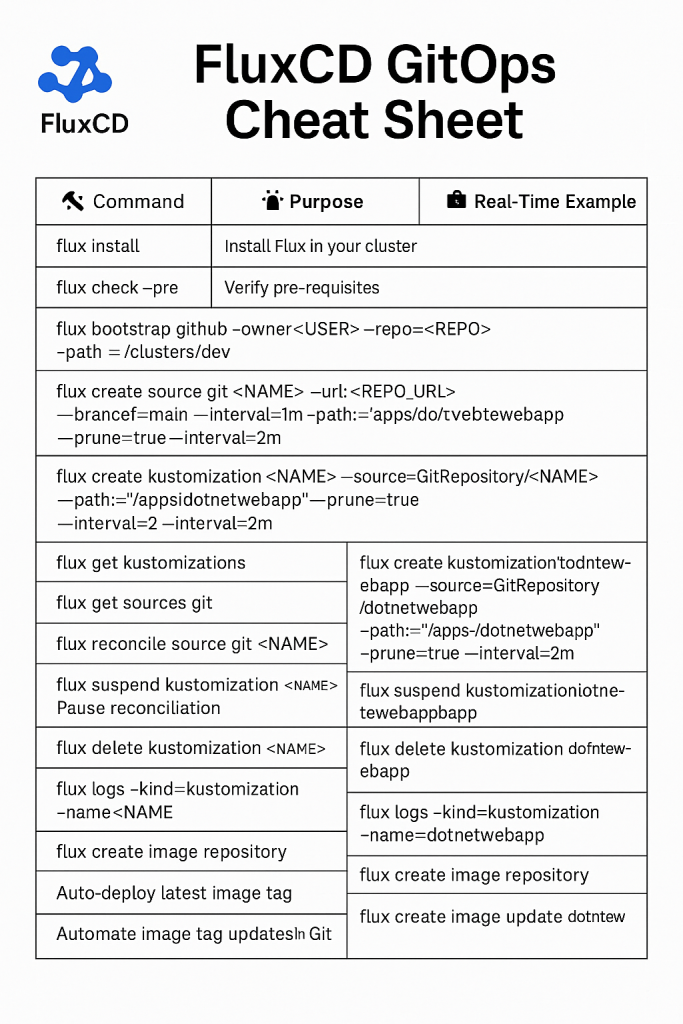
Basic Flux Commands
1. Bootstrap Flux in Your Cluster
flux bootstrap github \
--owner=jaganrajagopal \
--repository=DockercomposeNodejsMongodb \
--branch=main \
--path=./kubernetes \
--personalBusiness Purpose: This sets up Flux in your cluster and configures it to monitor the specified repository path. For the example repo, we’re pointing to a hypothetical ./kubernetes directory (note: the actual repo might need Kubernetes manifests added).
2. Check Flux Installation
flux checkBusiness Purpose: Verifies that Flux components are properly installed and healthy in your cluster.
3. List Flux Workloads
flux get allBusiness Purpose: Shows all Flux-managed resources (sources, kustomizations, etc.) in your cluster.
Example Workflow with the Sample Repository
Let’s imagine we’ve added Kubernetes manifests to the repository (currently it has Docker Compose files which would need conversion for Kubernetes).
4. Add a Git Source
flux create source git nodejs-app \
--url=https://github.com/jaganrajagopal/DockercomposeNodejsMongodb \
--branch=main \
--interval=1mBusiness Purpose: Tells Flux to monitor this Git repository for changes every minute. In a real business scenario, this automates deployments when developers push code changes.
5. Create a Kustomization
flux create kustomization nodejs-app \
--source=nodejs-app \
--path="./kubernetes" \
--prune=true \
--interval=5mBusiness Purpose: Applies Kubernetes manifests from the specified path. --prune removes resources that are no longer in Git, keeping your cluster perfectly in sync.
6. Trigger Reconciliation
flux reconcile kustomization nodejs-app --with-sourceBusiness Purpose: Forces Flux to immediately check for changes and apply them, rather than waiting for the next interval. Useful for testing.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
7. View Reconciliation Status
flux get kustomizationsBusiness Purpose: Check if your deployments are successfully synchronized with Git.
8. Check Logs
flux logs --all-namespacesBusiness Purpose: Debug issues when deployments aren’t working as expected.
9. Suspend Reconciliation
flux suspend kustomization nodejs-appBusiness Purpose: Temporarily stops automatic deployments, useful during maintenance or troubleshooting.
10. Resume Reconciliation
flux resume kustomization nodejs-appBusiness Purpose: Re-enables automated deployments after suspension.
Business Benefits in This Context
Using Flux with this Node.js/MongoDB example provides:
- Automated Deployments: When developers update the application code or Kubernetes manifests, changes are automatically deployed.
- Version Control: Every change is tracked in Git, providing an audit trail of who changed what and when.
- Consistency: The exact same deployment process runs in all environments (dev, staging, production).
- Disaster Recovery: Your entire infrastructure is defined in Git and can be recreated at any time.
- Security: Changes must go through Git, allowing code reviews and CI checks before reaching production.
